Which List Correctly Shows Carbohydrates In Size From Smallest To Largest?
3.5: Carbohydrates
- Page ID
- 16729
Where would we be without our jeans? They accept been the become-to pants for many people for decades, and they are still equally popular as ever. Jeans are made of denim, a type of cotton fiber fabric. Cotton is a soft, fluffy fiber that grows in a protective case around the seeds of cotton fiber plants. The cobweb is almost pure cellulose. Cellulose is the single nearly abundant biochemical compound found in Earth's living things and one of several types of carbohydrates.

What Are Carbohydrates?
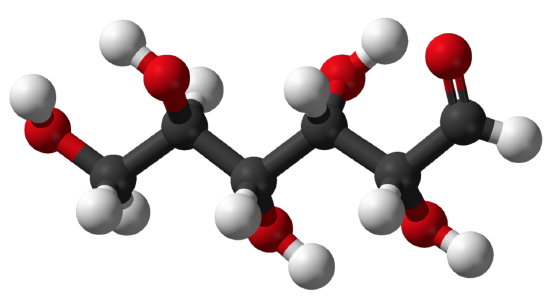
Carbohydrates are the most common form of biochemical compounds. They include sugars and starches. Carbohydrates are used to provide or shop energy, amid other uses. Like most biochemical compounds, carbohydrates are congenital of small repeating units, or monomers, which class bonds with each other to brand larger molecules, called polymers. In the instance of carbohydrates, the modest repeating units are known equally monosaccharides. Each monosaccharide consists of vi carbon atoms, as shown in the model of the monosaccharide glucose beneath.
Sugars
Sugars are the general proper name for sweet, short-chain, soluble carbohydrates, which are found in many foods. Their function in living things is to provide energy. The simplest sugars consist of a unmarried monosaccharide. They include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Glucose is a simple sugar that is used for energy by the cells of living things. Fructose is a unproblematic saccharide institute in fruits, and galactose is a elementary sugar establish in milk.
Other sugars incorporate two monosaccharide molecules and are called disaccharides. An example is sucrose or table carbohydrate. It is composed of one fructose molecule and one glucose molecule. Other disaccharides include maltose (two glucose molecules) and lactose (one glucose molecule and i galactose molecule). Lactose occurs naturally in milk. Some people can't digest lactose. If they potable milk, it causes gas, cramps, and other unpleasant symptoms unless the milk has been processed to remove the lactose.
Complex Carbohydrates
The uncomplicated sugars form the foundation of more complex carbohydrates. The cyclic forms of two sugars can be linked together by means of a condensation reaction. The figure beneath shows how a glucose molecule and a fructose molecule combine to class a sucrose molecule. A hydrogen atom from one molecule and a hydroxyl group from the other molecule are eliminated as water, with a resulting covalent bond linking the two sugars together at that point.
Glucose and fructose combine to produce the disaccharide sucrose in a condensation reaction equally shown in Effigy \(\PageIndex{three}\). Sucrose, commonly known as tabular array saccharide, is an example of a disaccharide.
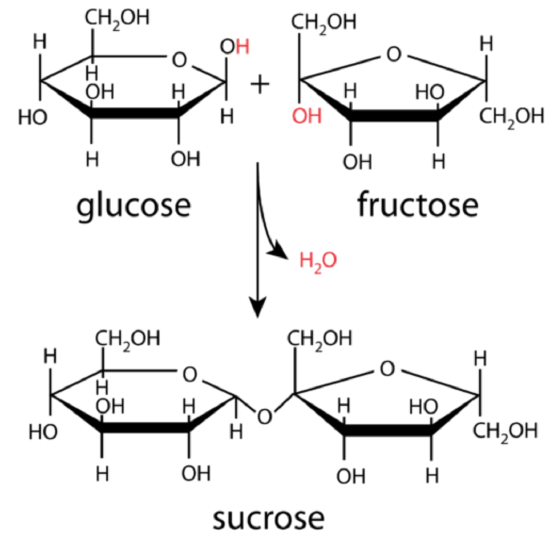
A disaccharide is a saccharide formed by the joining of two monosaccharides. Other mutual disaccharides include lactose and maltose. Lactose, a component of milk, is formed from glucose and galactose, while maltose formed from two glucose molecules. During digestion, these disaccharides are hydrolyzed in the small intestine to form the component monosaccharides, which are then absorbed beyond the intestinal wall and into the bloodstream to be transported to the cells.
Some carbohydrates consist of hundreds or even thousands of monosaccharides bonded together in long chains. These carbohydrates are called polysaccharides ("many saccharides"). Polysaccharides are as well referred to as complex carbohydrates. Complex carbohydrates that are found in living things include starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin. Each type of complex carbohydrate has different functions in living organisms but they generally either store energy or make upwardly certain structures of living things.
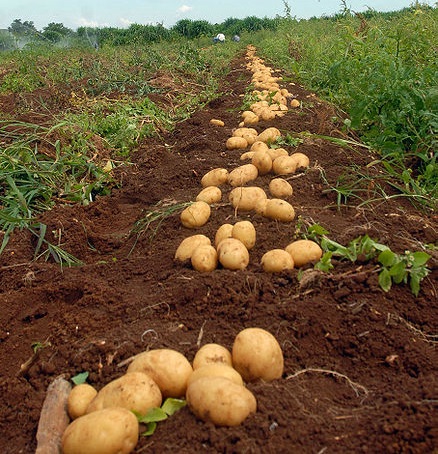



Starch
Starch is a complex carbohydrate that is made past plants to store energy. For example, the potatoes pictured below are packed full of starches that consist mainly of repeating units of glucose and other uncomplicated sugars. The leaves of potato plants make sugars by photosynthesis, and the sugars are carried to surreptitious tubers where they are stored every bit starch. When we eat starchy foods such as potatoes, the starches are broken downward by our digestive organisation to sugars, which provide our cells with free energy. Starches are hands and chop-chop digested with the assistance of digestive enzymes such as amylase, which is constitute in the saliva. If you chew a starchy saltine cracker for several minutes, you may start to gustation the sugars released equally the starch is digested.
Glycogen
Animals practise not store energy as starch. Instead, animals store the extra energy equally the complex carbohydrate glycogen. Glycogen is a polysaccharide of glucose. It serves equally a form of energy storage in fungi every bit well equally animals and is the main storage form of glucose in the human body. In humans, glycogen is fabricated and stored primarily in the cells of the liver and the muscles. When free energy is needed from either storage depot, the glycogen is cleaved downward to glucose for utilise past cells. Muscle glycogen is converted to glucose for use by muscle cells, and liver glycogen is converted to glucose for employ throughout the rest of the trunk. Glycogen forms an energy reserve that can be apace mobilized to run across a sudden need for glucose, but one that is less compact than the free energy reserves of lipids, which are the master class of energy storage in animals.
Glycogen plays a disquisitional part in the homeostasis of glucose levels in the blood. When claret glucose levels rise too high, backlog glucose can be stored in the liver by converting information technology to glycogen. When glucose levels in the blood fall as well low, glycogen in the liver tin can be broken down into glucose and released into the blood.
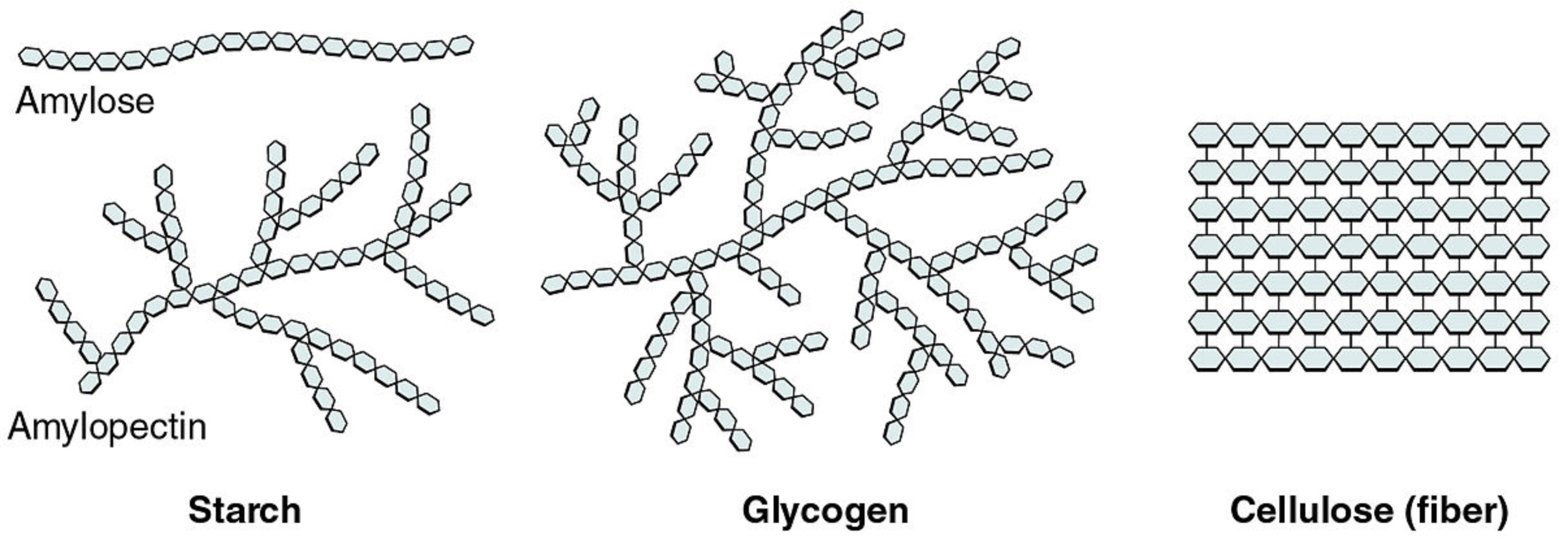
Cellulose
Cellulose is a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of linked glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the prison cell walls of plants and many algae. Man uses of cellulose include the production of cardboard and paper, which consist mostly of cellulose from wood and cotton fiber. The cotton fibers pictured below are virtually 90 percent cellulose.
Certain animals, including termites and ruminants such as cows, can assimilate cellulose with the assist of microorganisms that alive in their gut. Humans cannot digest cellulose, just it nonetheless plays an of import office in our nutrition. It acts every bit a h2o-attracting bulking agent for feces in the digestive tract and is oftentimes referred to equally "dietary cobweb."
Chitin
Chitin is a long-concatenation polymer of a derivative of glucose. It is plant in many living things. For case, it is a component of the cell walls of fungi, the exoskeletons of arthropods such as crustaceans and insects (including the beetle pictured in Figure \(\PageIndex{vii}\)), and the beaks and internal shells of animals such as squids and octopuses. The structure of chitin is similar to that of cellulose.

You probably know that you lot should eat plenty of cobweb, but exercise you know how much cobweb you need, how fiber contributes to skillful health, or which foods are good sources of cobweb? Dietary fiber consists mainly of cellulose, so it is found primarily in plant-based foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Dietary fiber tin can't exist broken downward and absorbed by your digestive system. Instead, it passes relatively unchanged through your gastrointestinal tract and is excreted in feces. That'due south how it helps go on you healthy.
The fiber in nutrient is ordinarily classified as either soluble or insoluble fiber.
- Soluble fiber dissolves in water to form a gel-similar substance as it passes through the gastrointestinal tract. Its health benefits include lowering claret levels of cholesterol and glucose. Skilful sources of soluble cobweb include whole oats, peas, beans, and apples.
- Insoluble fiber does not dissolve in water. This type of fiber increases the bulk of feces in the large intestine and helps keep food wastes moving through, which may help foreclose or correct constipation. Good sources of insoluble cobweb include whole wheat, wheat bran, beans, and potatoes.
How much fiber do you need for good health? That depends on your historic period and gender. The Institute of Medicine recommends the daily cobweb intake for adults shown in the table beneath. Most dietitians further recommend a ratio of about three parts insoluble fiber to i part soluble fiber each day. Most fiber-rich foods contain both types of fiber, then it usually isn't necessary to proceed track of the two types of fiber as long equally your overall cobweb intake is adequate.
Employ food labels and online fiber counters to find out how much total fiber you swallow in a typical day. Are you consuming enough cobweb for good health? If not, consider ways to increment your intake of this important substance. For example, substitute whole grains for refined grains, eat more legumes such every bit beans, and try to swallow at least v servings of fruits and vegetables each day.
| Gender | Age 50 or Younger | Historic period 51 or Older |
|---|---|---|
| Male | 38 grams | 30 grams |
| Female person | 25 grams | 21 grams |
Summary
- Carbohydrates are the most common class of biochemical compounds. The basic building block of carbohydrates is the monosaccharide, which consists of vi carbon atoms.
- Sugars are sweet, short-chain, soluble carbohydrates that are plant in many foods and supply united states of america with energy. Simple sugars, such every bit glucose, consist of just one monosaccharide. Some sugars, such as sucrose, or tabular array saccharide, consist of two monosaccharides and are chosen disaccharides.
- Complex carbohydrates, or polysaccharides, consist of hundreds or even thousands of monosaccharides. They include starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin. They by and large either store energy or course structures, such equally prison cell walls, in living things.
- Starch is a complex carbohydrate that is fabricated by plants to shop energy. Potatoes are a expert food source of dietary starch, which is readily cleaved downwards to its component sugars during digestion.
- Glycogen is a complex carbohydrate that is made past animals and fungi to store energy. Glycogen plays a critical part in the homeostasis of claret glucose levels in humans.
- Cellulose is the unmarried most mutual biochemical compound in living things. It forms the jail cell walls of plants and certain algae. Like near other animals, humans cannot digest cellulose, but it makes up most of the crucial dietary fiber in the human diet.
- Chitin is a complex sugar, similar to cellulose, that makes up organic structures such as the cell walls of fungi and the exoskeletons of insects and other arthropods.
Review
- What are carbohydrates? Describe their construction.
- Compare and contrast sugars and circuitous carbohydrates.
- Identify the four chief types of complex carbohydrates and their functions.
- If you chew on a starchy food such as a saltine cracker for several minutes, it may kickoff to taste sweet. Explain why.
- True or Faux. Glucose is mainly stored by lipids in the human torso.
- Put the following carbohydrates in order from smallest to largest: cellulose; fructose; sucrose
- Proper noun three carbohydrates that incorporate glucose every bit a monomer.
- Jeans are fabricated of tough, durable cotton. Explain how you lot think this material gets its tough qualities, based on what you know almost the structure of carbohydrates.
- Which exercise y'all retrieve is faster to digest — elementary sugars or circuitous carbohydrates? Explain your answer.
- True or False. Cellulose is broken down in the human digestive system into glucose molecules.
- Which type of fiber dissolves in water? Which type does non deliquesce in water?
- What are the similarities and differences between muscle glycogen and liver glycogen?
- Which carbohydrate is used directly by the cells of living things for energy?
- Which of the following is not a complex carbohydrate?
- chitin
- starch
- disaccharide
- none of the above
Explore More
- Body paint by Cuerpos Pintados, licensed CC Past ii.0 via Wikimedia Commons
- Glucose public domain via Wikimedia Commons
- Sucrose by Christopher Auyeung and Joy Sheng, CC BY-NC 3.0, via CK-12
- Potatoes past Elza Fiuza/ABr, licensed CC BY iii.0 via Wikimedia Commons Brazil
- Cotton by KoS, released into the public domain via Wikimedia Commons
- X-lined June beetle by Junkyardsparkle, dedicated CC0 via Wikimedia Commons
- Three Polysaccharides by OpenStax College, licensed CC Past 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons Brazil
- Beans by Charles Brooking, released into the public domain via Wikimedia Commons
- Text adapted from Human Biological science by CK-12 licensed CC By-NC iii.0
Which List Correctly Shows Carbohydrates In Size From Smallest To Largest?,
Source: https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Human_Biology/Book:_Human_Biology_%28Wakim_and_Grewal%29/03:_Chemistry_of_Life/3.05:_Carbohydrates
Posted by: maguirepeetruse.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which List Correctly Shows Carbohydrates In Size From Smallest To Largest?"
Post a Comment